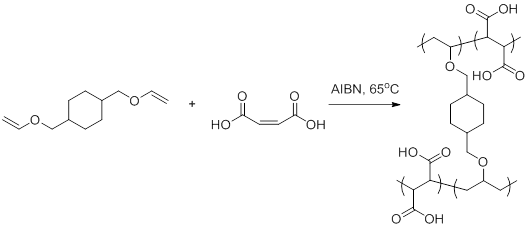
In order to overcome the challenge of direct radical polymerization of vinyl ethers commercial hydroxy functional vinyl ethers such as 2 hydroxyethyl vinyl ether heve were subjected to free radical polymerization generating.
Vinyl ethers radical.
It can be initiated with peroxide azo and redox initiators.
They are increasingly used in radiation curing systems because of a lower toxicity profile than the commonly used acrylic monomers.
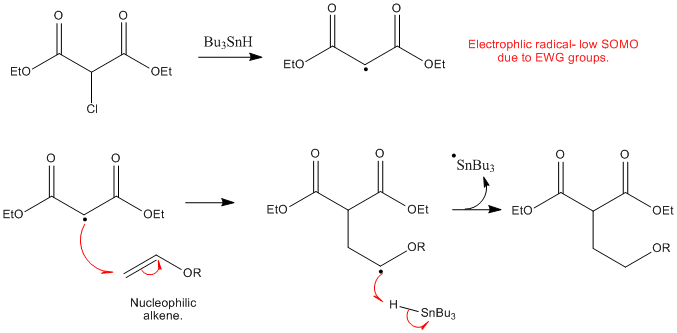
The radical produced by attack of a thiyl radical on the terminal methylene of the vinyl ether is stabilised by the oxygen atom of the ether group and therefore it is not surprising to find that vinyl ethers are very reactive ene components of the thiol ene reaction 4 the ether substituent on the double bond reduces the ionisation potential of.
It is remarkable that only 10 addition of dve 3 increases the conversion of the acrylate from.
Vinyl ethers undergo radical initiated copolymerization in the presence of specific monomers such as maleates fumarates and acrylics.
Teator and leibfarth report a general protocol to polymerize a variety of such vinyl ethers isotactically see the perspective by foster and o reilly.
Vinyl ether radical figure 5.
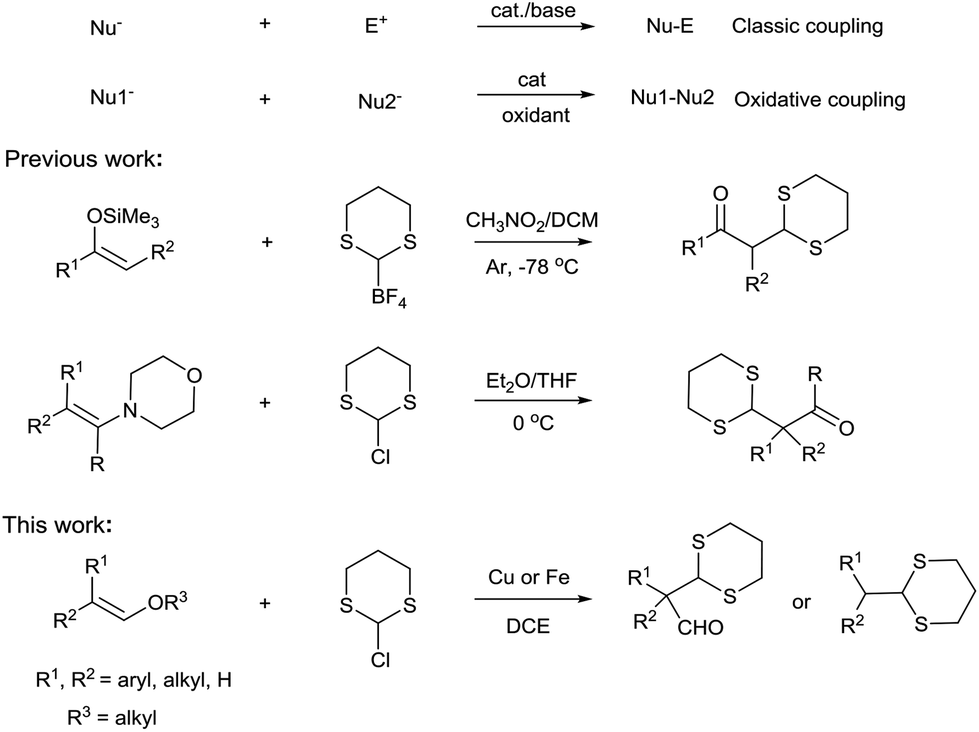
This reaction is accepted as a click chemistry reaction given the reactions high yield stereoselectivity high.
The product is used as low viscosity and fast curing monomers in cationic polymerization applications and as low viscosity monomers in radical polymerization applications.
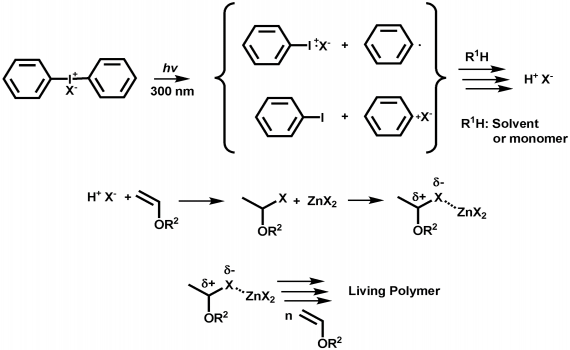
Vinyl ethers undergo homopolymerization via a cationic mechanism.
Vinyl ethers 1 which have a strongly electron donating alkoxy substituent readily form polymers on treatment with an acidic compound initiator the polymerization is thus cationic in nature.
They rely on a chiral.
Polymerization rate in figure 5 the conversion of acrylate 1407 cm 1 and vinyl ether groups 1618 cm 1 are plotted as a function of vinyl ether content.
Copolymerization components include vinyl chloride vinyl acetate acrylic metacrylic acids and their ethers maleic anhydrides fluorinated olefin such as f2c cf2 and.
Well optimized catalysts produce vast quantities of isotactic polypropylene in which the side chains all face the same way.
However the polymerization under free radical conditions gives only low molecular weight oligomers and only copolymers can be synthesized.
Free radical copolymerization of vinyl ethers is also possible.
No anionic or radical polymerizations give high polymers from vinyl ethers except for the alternating radical copolymerization with an electron deficient monomer.
Add an oxygen into the monomer though and that degree of uniformity becomes harder to enforce.